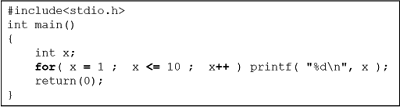Hello Everyone.... Welcome to My Blog!!!
In My Blog I am going to write about Coding especially for C !!!
And Today I am going to discuss about
Repetition in Coding.
So what's Repetition??
Repetition in Coding is know as Looping, while Looping is a sequence of statements which is specified once but which may be carried out several times in succession. The number of looping can be predefined (hard - coded in program) or defined later at run time.
And there are three in C that are designed for Looping :
1. The for statement
2. The while statement
3. The do-while statement
Let's Discuss one by one!!
The for Statement
The general form / syntax of the for statement is like this:
for (expression1; expression2; expression3) {
statement1;
statement2;
}
The for statement first evaluates expression1, which usually initializes one or more variables. In other words, expression1 is only evaluated once when the for statement is first encountered.
The second expression, expression2, is the conditional part that is evaluated right after the evaluation of expression1 and then is evaluated after each successful looping by the for statement. If expression2 returns a nonzero value, the statements within the braces are executed. Usually, the nonzero value is 1. If expression2 returns 0, the looping is stopped and the execution of the for statement is finished.
The third expression in the for statement, expression3, is not evaluated when the for statement is first encountered. However, expression3 is evaluated after each looping and before the statement goes back to test expression2 again.
And here is the example in C :
#include <stdio.h>
int main (){
int j;
for (j = 1; j < 10; j++){
printf ("Hello");
printf("\n")
}
return(0);
}
So in that Coding we can read that " j " is a Integer, and inside the for in expression one it means Integer " j " is starting from number 1. Then the second expression means that the Maximum Integer for " j " is no more than 10. After that the third expression means that " j " is going to be add by 1 number until it got the maximum of expression 2. And after the number is maximum, the program is going to execute 9 word "Hello" (without quotation) because it is commanded to write Hello.
So if I am going to make a sentence of that coding is "For j is same with one and j is lower than 10, then I am going to add more number until it is 9, after that I finally could write word "Hello" 9 times.
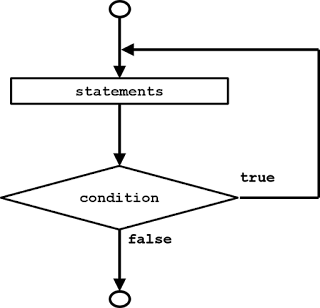
The Flow Chart of For is like this:
And here is some program to print out number 10 to 1
While the program to print out 1 to 10 is like this :
There is 2 type of Loop:
1. Infinite Loop
2. Nested Loop
Infinite Loop is Loop with no stop condition can use “for-loop” by removing all parameters (exp1, exp2, exp3). To end the loop use break.
Nested Loop is Loop in a loop, the repetition operation will start from the inner side loop.
Example:
The While Statement
What is the while repetition statement??
The while statement is also used for looping. Unlike the situation with the for statement, there is only one expression field in the while statement.
The general form / syntax is like this :
while (expression) {
statement1;
statement2;
}
exp is
Boolean expression. It will result in true (not zero) or false (equal to zero).
Statement
will be executed while the exp is
not equal to zero.
exp evaluation is done before the
statements executed.
Here expression is the field of the expression in the while statement. The expression is evaluated first. If the expression returns a nonzero value (normally 1), the looping continues; that is, the statements inside the statement block are executed. After the execution, the expression is evaluated again. The statements are then executed one more time if the expression still returns nonzero value. The process is repeated over and over until the expression returns 0.
And here is the Example in C :
#include <stdio.h>
int counter = 1;
while ( counter <= 10 ) {
printf( "%d\n", counter );
++counter;
}
So in that coding we can read that "Integer counter is starting from 1, While integer counter is lower than 10, write "number till 10" / add more number until 10. Example : ((+1)*9).
So yeah... it's a little bit different with For and the difference is on the ++ placement, while "for statement" ++ placement is after "Lower than" Command. But for "while statement" the ++ command is after the printf.
The Flow Chart While is like this :
The Do-While Statement
What is Do-While Statement??
Do - While, which puts the expressions at the bottom of the loop. In this way, the statements controlled by the do-while statement are executed at least once before the expression is tested. Note that statements in a for or while loop are not executed at all if the condition expression does not hold in the for or while statement.
The general form / syntax is like this :
do {
statement1;
statement2;
} while (expression);
Keep executing while exp is true
exp evaluation done after executing the statement(s)
Here expression is the field for the expression that is evaluated in
order to determine whether the statements inside the statement block
are to be executed one more time. If the expression returns a
nonzero value, the do-while loop continues; otherwise,the looping
stops.
And here is the Example in C :
#include <stdio.h>
int counter=0;
do {
printf( "%d ", counter );
++counter;
} while (counter <= 10);
So in that Coding we can read that "Integer counter is start from 0, do write number while adding more number one by one and while counter is less than 10").
Yeah it seems like it's not really different from For and While, But in the Do-While ends with a semicolon, which is an important distinction from the if and while statements. And in Do-While we are writing the word first before counting the maximum word can be placed.
The Flow Chart Do - While is like this :
The Repetition Operation
In while operation, statement block of statements may never be executed at all if exp value is false
In do-while on the other hand statement block of statements will be executed min once
To end the repetition, can be done through several ways:
–Sentinel
–Question, should the repetition continue?
As sentinel, used 0 for width or height
Break and Continue Operation
Break is to force finish the loop (for, while, do-while), and to end the switch operation.
Continue skip all the rest of statements (subsequent to the skip statement) inside a repetition, and continue normally to the next loop.
And so the Summary for Repetition is a condition which is one or more instruction repeated for certain amount of time.
So yeah... That's all about Repetition / Looping in Coding especially C++, how was it?? you understand right??
Thank for reading this Blog and You are Free to Comment on the comment section below.
Good Bye!!!
References:
Paul Deitel& Harvey Deitel. (2016). C how to program : with an introduction to C++. 08. Pearson Education. Hoboken. ISBN: 9780133976892. Chapter 3 & 4